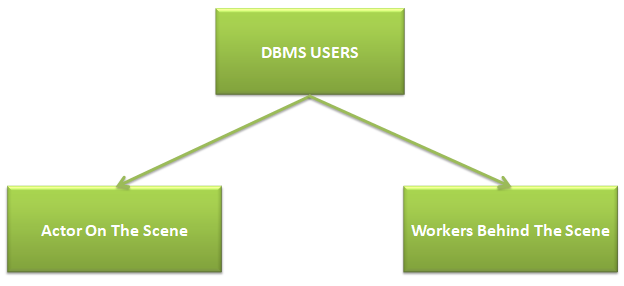
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a powerful tool for organising and managing information, but its success depends on the diverse roles of individuals who interact with it. These users fall into two broad categories: the actors on the scene, who directly utilize the database for daily tasks, and the workers behind the scene, who design, maintain, and ensure the system’s functionality. Understanding these different types of DBMS users is crucial for effectively managing and leveraging your database resources.
Actors on the Scene: The Users Who Bring Data to Life
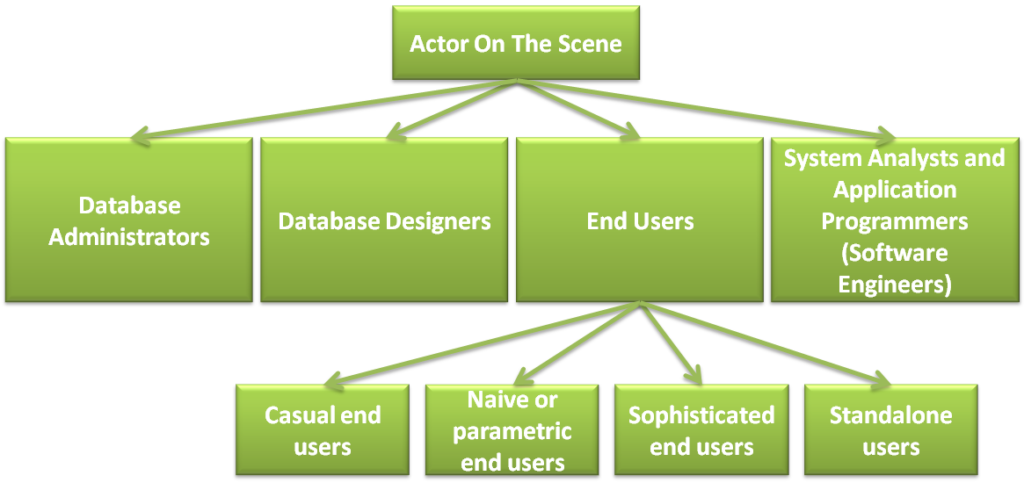
- Database Administrators (DBAs): The guardians of the database, DBAs have comprehensive authority and responsibility. They control access, monitor performance, and safeguard data integrity.
- Database Designers: The architects of the data world, database designers craft the structure of the database, defining how data is organised and stored. They work closely with users to understand their needs and translate them into efficient data models.
- End Users: The most diverse group, end users interact with the database to fulfill various needs. This category encompasses:
- Casual End Users: Occasionally access the database for specific information.
- Naive or Parametric End Users: Frequently query and update the database using pre-defined operations.
- Sophisticated End Users: Power users who leverage advanced query languages and tools to analyze data.
- Standalone End Users: Maintain personal databases using user-friendly software.
- System Analysts and Application Programmers: These professionals act as intermediaries between end-users and the database. They gather requirements, design user interfaces, and develop applications that interact with the DBMS.
Workers Behind the Scene: The Unsung Heroes of Database Systems
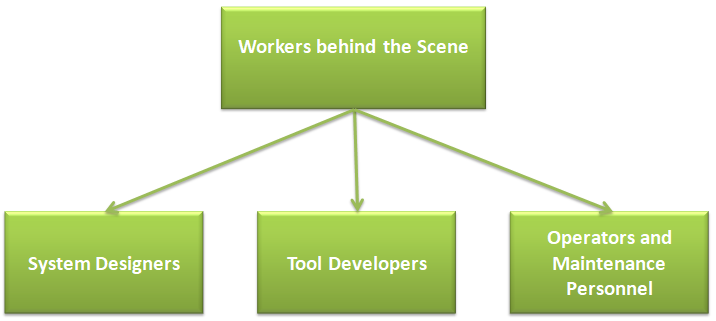
- DBMS System Designers and Implementers: These technical experts create and build the DBMS software itself,including its modules, interfaces, and functionalities. They ensure the system is robust, secure, and efficient.
- Tool Developers: This group focuses on creating additional tools that enhance the DBMS experience. These tools can assist with database modeling, performance monitoring, data visualization, and more.
- Operators and Maintenance Personnel: Responsible for the day-to-day operation and maintenance of the database system and its underlying hardware and software environment. They ensure the system is available,reliable, and performing optimally.
The Importance of Collaboration Among DBMS Users
The success of a DBMS relies on effective collaboration between these diverse user groups. DBAs must understand the needs of end-users and work with designers to create a database that meets those needs. System analysts and programmers translate those requirements into functional applications. Meanwhile, the workers behind the scene ensure that the entire system runs smoothly and reliably.
FAQs: Different Types of DBMS Users
Q: Who is responsible for data security in a DBMS?
A: Primarily, the Database Administrator (DBA) is responsible for implementing and maintaining security measures, but all users play a role in protecting data.
Q: What skills do I need to become a database designer?
A: Database designers need strong analytical and problem-solving skills, knowledge of data modelling techniques, and familiarity with database technologies.
Q: Can end-users access the database directly?
A: Yes, but the level of access and the tools they use depend on their category. Casual users might use basic query interfaces, while sophisticated users may write complex SQL queries.
Q: What is the role of tool developers in a DBMS environment?
A: Tool developers create additional software applications that enhance the functionality of the DBMS, such as design tools, performance monitors, and data visualisation tools.